Research Germany Branchen Reports (Part 2)
The mechanical engineering industry in Germany: turnover, statistics, background
Germany ranks third among the world’s market leaders in machinery and plant engineering, with around 11% of global machine production. Internationally, Germany is characterised as a nation with “hidden champions” due to its medium-sized market structure. The approximately 20,000 German mechanical engineering companies have a strong export surplus of approx. 17%, with an increasing export quota of 79% from an import quota of 62% [1]. In terms of the labour market, mechanical and plant engineering is the most important industrial employer in Germany, employing around 1.36 million people [2]. The total turnover of the top 100 German mechanical engineering companies in 2018 was around €228 billion. The following industry report provides detailed insights into the fields of activity and innovations in the engineering sector, the most important locations, key financial figures, and insights into the gender ratio and efforts in the field of sustainability.
Components of our mechanical engineering market analysis
1) Fields of activity of the German mechanical engineering industry: What is produced?
Although the mechanical engineering industry can be divided into various specialist areas, these are very broadly diversified. Agricultural engineering, construction machinery, materials handling, measuring and testing technology, precision engineering, robotics and automation as well as packaging machines are just a few of many. In 2018, the top-selling sectors in terms of turnover were machine tools (~€23 billion), drive technology (€20 billion), materials handling (~€18 billion), packaging technology (~€18 billion) and mining and building material machinery (~€14 billion) [3, 4]. In order to give an overview of this very broad sector, these high turnover areas are presented below.
Machine tools – milling machines, presses, machine hammers etc.

Image Source: Siemens
Machine tools are machines for manufacturing workpieces with tools whose movement to each other is predetermined by the machine [4]. These include lathes and milling machines, erosion machines, mechanical presses and machine hammers. There are also many subcategories – therefore machine tools are divided according to forming, separating or joining production processes and their degree of automation. The Siemens AG is one of the top 5 mechanical engineering manufacturers in Germany and also produces machine tools, among other things. The group has divided up this “Machine Tool Systems” area in 5 different sectors: automotive, aerospace, electronics, power generation and tool and mould making. The trend in all sectors is towards automation and digitalisation.
Drive technology – motors and gears, (electronic) hydraulic systems etc.
Image Source: rexroth
In general, drive technology deals with systems that generate movement by power transmission. This area is highly complex and, in addition to the energy supply, deals with the realisation of motion sequences in order to guarantee the smooth control of various elements. Drive technology goes hand in hand with mechatronics – in addition to electric drives, this sub-area is responsible for electrohydraulics and -pneumatics. The John Deere GmbH & Co. KG manufactures a wide range of engines and transmissions: in addition to generator drive motors, industrial motors and marine engines, the GmbH also offers drive train components. A subsidiary of Robert Bosch GmbH, the rexroth Company is market leader for electric drives and controls. The subcontractor focuses on the fields of electrical drives and controls, hydraulics, linear and assembly technology and related services. The GmbH is a market driver for servo drives and advertises with the most powerful CNC (Computerized Numerical Control) and motion control systems.
Conveying technology – conveyor belts, lifting and turning systems etc.

Image Source: Siemens
Conveyor technology describes the discipline of conception, design, planning and execution of conveyors for conveying unit loads. This segment takes place in closed areas, such as in mining, ports, airports or even in industrial areas. The Kion Group AG benefits from the globalisation of value and supply chains and is the largest European and second largest global manufacturer of industrial trucks. The world leading brands of the STILL, DEMATIC, BAOLI and OM Volters group offer a wide range of products in various segments such as forklift trucks, warehouse equipment and complete warehouse systems. The AG is therefore the technology leader in this sector. The Siemens Group is in this segment and again divides up its product range in this area: intralogistics, automotive, food and beverages and airports. The largest product area is various conveyor belts, plus various lifting and rotating mechanisms and sorting systems.
Mining and building material machinery

Image Source: thyssenkrupp
The mining sector is again a very diverse area within the mechanical engineering industry. Starting with crushing systems, storage- and sorting systems, required structures range all the way to the packaging of the final product. Systems and machines for the mining industry include bucket wheel excavators, belt wagons, conveyor systems and spreaders. One of the most important systems are crusher-belt systems, where the German thyssenkrupp AG is one of the market leaders worldwide. In the building materials sector, the Group focuses on the manufacture and improvement of cement plants and offers both individual machines, equipment and systems and complete plants. In this segment, the AG is known for “green cement” – read more under sustainability.
Packaging Technology

Image Source: krones
Packaging technology generally refers to methods for making products transportable as packaged goods. The Krones AG is among the top 10 German mechanical engineering manufacturers and the market leader in filling and packaging technology. The focus here is on the beverage segment. Founded in 1951, the company covers an integrated process with production, filling and packaging products. Even the somewhat smaller company Windmöller & Hölscher KG
mainly manufactures machines and systems in the packaging sector, dividing them into three areas: extrusion, printing and converting.
A detailed list of German mechanical engineering companies and their segments is provided by our List of the 500 largest mechanical engineering companies in Germany.
Innovations, trends and growth drivers in the industry

Bildquelle: thyssenkrupp
One of the greatest strengths of the German mechanical engineering sector is its technological advantage. In addition to low competitiveness in the manufacture and sale of special machinery, German mechanical engineering has an excellent image for high-quality products. The reinforcement of this leading position is one of the industry’s greatest opportunities. The big buzz word that often falls in the mechanical engineering sector is “Industry 4.0”. Industry 4.0 is characterised by digitalisation, automation and interconnection. This term includes monitoring systems that identify sources of error in advance, the evaluation of user data or the digitalisation of internal processes. Industry 4.0 is resource-saving and efficient. If chips are attached to products which are read by fully automated machines, the next production steps can be anticipated and, for example, missing parts can be reordered independently. Entire storage systems are fully automated and run via closely networked systems. This is where another buzz word comes into play: “Integrated Industry” describes precisely this interconnection and increasingly better coordinated systems. Instead of individual machines, system solutions are manufactured and offered in which the individual machines are perfectly coordinated. This leads to the so-called “batch size 1”: Individual products that are created entirely according to the customer’s wishes. The uniqeness: Thanks to modern production facilities, special products can now be manufactured at the cost of series production. Important for this are Big Data technologies, which are able to continuously identify internal and external processes with optimisation potential by analysing huge amounts of machine and customer data. Of particular interest here are the so-called “digital twins” – digital presences of possible machines or entire production plants. This IoT technology makes it possible to identify sources of error and potential for optimisation before the actual production of machines, thus saving a lot of money.
An insight into the industry of the future is presented by the Siemens Plant in Amberg. The electronics factory has already been awarded the Industry 4.0 Award several times in the category “Smart Factory”. Dashboards are used to collect and evaluate performance, product and quality data from all machines. With the help of this internal factory data and the artificial intelligence there, zero-defect production is no longer a vision, but a fixed goal, according to the plant manager, Dr. Gunter Beitinger. In addition to digital twins, collaborative robots, driverless transport systems and 3D printing, Siemens relies on the in-house open cloud system “Mindsphere” [7].
2) Map of engineering companies: Where is the production?
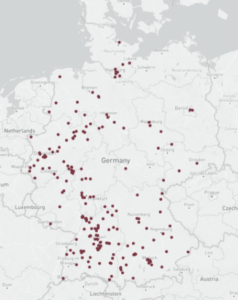 Mechanical Engineering Cluster in Germany: Industrial Centre Baden-Württemberg
Mechanical Engineering Cluster in Germany: Industrial Centre Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg is the most important industrial employer and location with more than 348,000 employees, a turnover of € 85.4 billion and over 1/3 of the largest German mechanical engineering companies. What is the reason for this? The mechanical engineering industry in Baden-Württemberg invests an average of 6% in research and development. This is worthwhile: Machinery from the region is in demand worldwide, and its position as Germany’s technology leader is undisputed. To ensure that stays as it is, 5% of turnover is invested in training and further education. Teaching and research is very important for the science location. In addition to basic research, the universities and training companies located there provide innovative and future-oriented training. Under the initiative “Alliance Industry 4.0”, competences are bundled and jointly worked towards a digitalised future. Another major advantage is the strong networking between mechanical engineering companies and suppliers – Baden-Württemberg consists of many clusters [8].
Lists matching this industry report
-
€399,99 Incl. VAT
-
Rated 4.50 out of 5€1.499,99 Incl. VAT
-
Rated 5.00 out of 5€299,99 Incl. VAT
-
Rated 5.00 out of 5€349,99 Incl. VAT
-
Rated 5.00 out of 5€2.499,99 Incl. VAT
3) Key financial figures for the engineering industry: What is the market volume?
Market volume
Companies with turnover below €1 billion (2018)
Sales development of the top 5
The figures are based on our database and can be found in the list of the top 200 mechanical engineering companies in Germany. Only companies whose product portfolio can be assigned to the mechanical engineering industry as a whole are presented. As a result, Siemens AG and thyssenkrupp AG, which are among the largest German mechanical engineering companies in Germany, are not included.
Market volume and total sales in the German machinery industry: 2015-2018
With a growth rate of 4.3% (2017-2018), the German market was even above the global growth rate of 4%. However, the mechanical engineering market is a global market – the German export ratio in 2018 was 79%, the import ratio 62% [1]. The German industry is therefore dependent on functioning global integration. This internationality is on the brink of collapse – the Brexit, the global economic downturn and the trade dispute between the USA and China have left their mark: VDMA chief economist Dr. Ralph Wiechers predicts a 2% drop in real output by 2020. The downturn will be cushioned by a good order backlog of 8.4 months and stable capacity utilisation of almost 87%. The economist is also optimistic about the opportunities offered by Industry 4.0, digitalisation, CO2-neutral production and new forms of mobility [9].
The graphs are based on our list of the top 500 mechanical engineering companies in Germany. As our database contains the total turnover of the companies, there may be deviations from the figures on turnover only in the mechanical engineering sector.
Competition analysis: What is the market structure in the engineering industry?
The mechanical engineering sector in germany is characterised by medium-sized companies: excluding the 3 largest companies (Bosch, Siemens and thyssenkrupp), the average number of employees in the 100 largest german companies is 4,009. the majority of the companies (72% of the top 100) have annual sales of less than € 1 billion. The companies are often family-run. The mechanical engineering sector is also very heterogeneous and includes everything from parts producers to plant manufacturers. 2015-2018 the three largest German mechanical engineering companies (Robert Bosch, Siemens and thyssenkrupp) were accounted for just over 60% of the total market volume.
Development of the German market leaders in the engineering industry
The Kion Group, which was only spun off from Linde AG in 2006, is one of the leading mechanical engineering companies in Germany. The company is the second largest supplier of forklift trucks and warehouse equipment in the world and the market leader for industrial trucks in Europe. With over 34,000 employees, the AG is active in more than 100 countries with plants, research and development centres as well as sales and service units. Its product portfolio is divided into two parts: Industrial Trucks & Services and Supply Chain Solutions.In the field of supply chain and automation solutions the brand Dematic is the leading supplier.
The GEA Group Aktiengesellschaft was founded as early as 1881 and produces process technology and components with its 250 subsidiaries operating worldwide, primarily in the food and beverage industry. The company is divided into five divisions: Seperation & Flow technologies, Farm technologies, Liquid & Powder technologies, Food & Healthcare technologies and Refrigeration technologies. In these divisions, around 18,000 employees generate annual sales of around €5 billion. At around 80% the food, beverage and pharmaceutical industries account for the largest share of this.
The Enercon GmbH is the largest German manufacturer of wind turbines; in 2017 Enercon was among the five largest manufacturers worldwide. Founded in 1984, the GmbH has sold and installed almost 28,000 wind turbines worldwide under the motto “Energy for the World”. With annual sales of around €5 billion in over 45 countries, the company claims to be one of the world leaders in its segment. Production is kept local – over half of the turbines are manufactured in Germany.
The Krones AG is a manufacturer of systems and machines for the production, filling and packaging of beverages and liquid food products. Based in Neutraublingen, Germany, the company employs over 17,ooo people and generates an annual turnover of ~4 billion €. The AG generates 90% of this turnover abroad, 50% of which is generated in emerging markets. Krones offers a holistic product portfolio: Starting with products and systems for production, through filling processes, packaging solutions, cleaning systems and even transport, the company offers everything.
4) Gender balance and sustainability
Share of women on management board
Gender distribution in the mechanical engineering industry
The proportion of women on management boards in the German mechanical engineering sector is 3.26%. According to the Federal Statistical Office, the national average of female executives is 30%, although this figure includes supervisory boards. Looking at the top 5 in the large mechanical engineering industry in Germany (Robert Bosch GmbH, thyssenkrupp AG, Siemens AG, John Deere GmbH & Co. KG and GEA Group AG), only one of 26 managing directors is female.
The data for the graphics and text are taken from our database and refer exclusively to the (managing) directors.
Sustainability in the German mechanical engineering industry:
In the PWC study “Think strategically, act sustainably and measure success” from 2014, the auditor examined the importance of sustainability in the German mechanical and plant engineering industry. The survey questioned 100 managers from the industry. The result of the study: sustainability is gradually gaining in importance, but a comprehensive approach is not yet available. What has changed to date? In the following, we present the most important sustainability areas in the mechanical engineering industry and present concrete examples and implementations.
 The Krones AG is a perfect example of a sustainable approach within its product portfolio. The company offers a wide range of machines and systems that have one goal in mind: resource conservation and recycling. The company stands for the approach to make plastics sustainable through holistic recycling. To this end, Krones offers machines and systems for preforms, containers, secondary packaging, used PET bottles and, finally, recycled material – under the name MetaPure these recycling solutions are combined. The sustainability programme launched by Krones AG in 2008 is named enviro uand ensures a sustainability standard for Krones machines, systems and, since 2019, for packaging as well. According to the company, Enviro-certified products meet at least the EME standards (Energy and Media Efficiency, Environmental Sustainability) and “thus fulfil all the requirements for environmentally friendly, energy- and media-efficient production”. A good example is the new product “LitePac“with which the company offers a machine that produces an alternative to foil binding.
The Krones AG is a perfect example of a sustainable approach within its product portfolio. The company offers a wide range of machines and systems that have one goal in mind: resource conservation and recycling. The company stands for the approach to make plastics sustainable through holistic recycling. To this end, Krones offers machines and systems for preforms, containers, secondary packaging, used PET bottles and, finally, recycled material – under the name MetaPure these recycling solutions are combined. The sustainability programme launched by Krones AG in 2008 is named enviro uand ensures a sustainability standard for Krones machines, systems and, since 2019, for packaging as well. According to the company, Enviro-certified products meet at least the EME standards (Energy and Media Efficiency, Environmental Sustainability) and “thus fulfil all the requirements for environmentally friendly, energy- and media-efficient production”. A good example is the new product “LitePac“with which the company offers a machine that produces an alternative to foil binding.
 Energy efficiency is a very big issue in the mechanical engineering industry – for example, energy consumption accounts for around 60% of the production costs of food, an important customer for the mechanical engineering industry. Proper refrigeration, storage and logistics is also a major problem in the food industry, resulting in the waste of around 30-50% of the food produced worldwide. The GEA Group offers innovative solutions for this. A ventilation control system feeds coolants into the evaporator, thus reducing energy requirements by up to 30%. A heat pump technology has enabled a plant to save as much as 70% of the energy consumed in a drying process. Also interesting is the CALLIFREEZE® System of the AG. Especially in the food industry it is important to maintain the required maximum temperatures. If a product that has already reached or fallen below the optimum temperature is cooled further, this is inefficient and wastes energy. With sensor technology, the temperature can now be permanently monitored, the optimum temperature can be maintained and energy savings of up to 15% can be achieved.
Energy efficiency is a very big issue in the mechanical engineering industry – for example, energy consumption accounts for around 60% of the production costs of food, an important customer for the mechanical engineering industry. Proper refrigeration, storage and logistics is also a major problem in the food industry, resulting in the waste of around 30-50% of the food produced worldwide. The GEA Group offers innovative solutions for this. A ventilation control system feeds coolants into the evaporator, thus reducing energy requirements by up to 30%. A heat pump technology has enabled a plant to save as much as 70% of the energy consumed in a drying process. Also interesting is the CALLIFREEZE® System of the AG. Especially in the food industry it is important to maintain the required maximum temperatures. If a product that has already reached or fallen below the optimum temperature is cooled further, this is inefficient and wastes energy. With sensor technology, the temperature can now be permanently monitored, the optimum temperature can be maintained and energy savings of up to 15% can be achieved.
5) Statistics and facts in the mechanical engineering sector
- The most important and highest-turnover segments in the engineering industry are
- Machine Tools
- Drive Technology
- Conveying technology
- Mining and building material machinery
- Packaging Technology
- Innovations and growth drivers in the mechanical engineering industry:
- digitalisation
- Automation
- Networking
- Digital Twins
- Baden-Württemberg has the largest number of mechanical engineering companies in Germany – this traditional location relies on high spending on R&D and education
- Die Hoffnung für eine weiterhin wachsende Branche liegt auf der Industrie 4.0, der Digitalisierung und CO2-neutraler Produktion
- The hope for a continued growth of the sector is based on Industry 4.0, digitalisation and CO2-neutral production
- The market structure is medium-sized and often family-run
- At 97%, the management is predominantly male
- Recycling, holistic resource use and energy efficiency are key sustainability issues for German mechanical engineering companies
Sources (last accessed on 16.06.2020)
[1] https://www.dsgv.de/content/dam/sparkasse/downloads/firmenkunden/maschinenbau.pdf
[2] https://arbeitsmarkt.vdma.org/
[3] https://www.ingenieur.de/karriere/branchenprofile/maschinen-und-anlagenbau/#teilbereiche
[4] Reimund Neugebauer (Hrsg.): Werkzeugmaschinen: Aufbau, Funktion und Anwendung von spanenden und abtragenden Werkzeugmaschinen. Springer, 2012, S. 4.
[6] https://www.vdma.org/documents/105628/5713207/Branchenbericht CSR Maschinenbau 2014/65467c34-e7ab-4cf9-866c-37f846d93787
[9] https://www.vdma.org/v2viewer/-/v2article/render/41721593
Iconsource (last accessed on 16.06.2020): https://www.flaticon.com/de/autoren/freepik